Key takeaways
- A cardiac catheterization laboratory is an area in a hospital with technology used to diagnose & treat heart conditions.
- Patients go to the cath lab for a range of reasons, including minimally invasive procedures for diagnosing & treating heart conditions, and diagnosing & treating irregular heartbeats.
- Cath labs are staffed 24/7 with highly trained, well experienced heart providers who are focused on helping your heart be at its healthiest.
Heart patients who need to be seen for diagnosis, imaging, or other minor procedures may be sent to a cardiac catheterization laboratory, also called a cath lab.
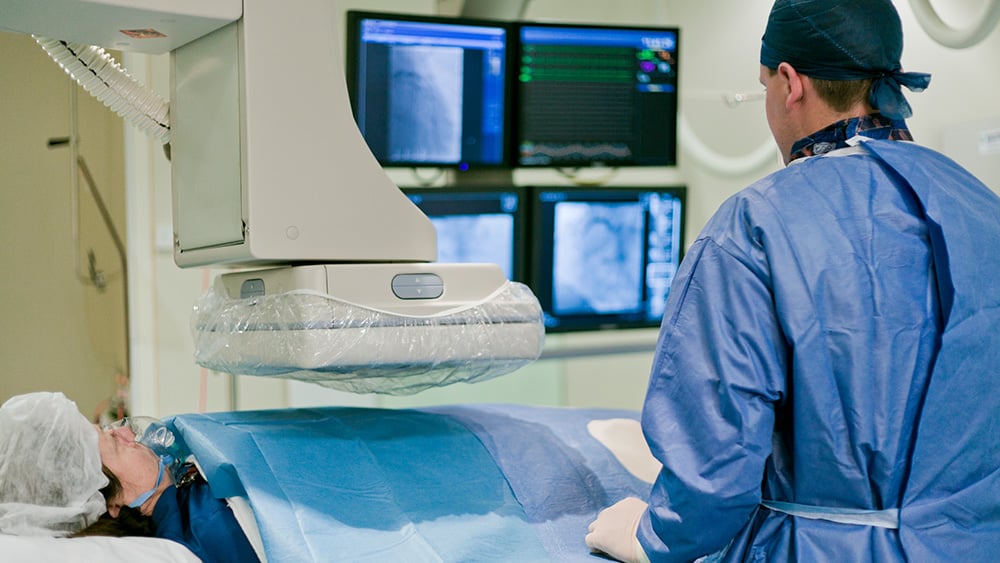
The cath lab is an area of a hospital with imaging technology that is used to diagnose and treat many types of heart conditions. Patients of all kinds, from elective procedures to emergency situations, come in for treatment each day.
Michael Macikowski, PA-C, works with the Structural Heart and Interventional Cardiology team in the cath lab at Rochester General Hospital. He explains how the cath lab operates, which providers you can expect to see there, and the types of procedures performed.
Who works in a cath lab?
All of the healthcare providers who work in a cath lab are specifically trained in cardiology. This includes:
- cardiologists
- physician assistants (PAs)
- nurse practitioners (NPs)
- nurses
- radiology technologists
- cardiac sonographers
Providers see patients during regular hours Monday through Friday for elective procedures. If there is an urgent need for a procedure, an on-call team is always available to treat patients.
What types of procedures or tests are performed in a cath lab?
Structural heart/interventional procedures
Right heart catheterization: A test where a special catheter is guided through your veins into the right side of the heart and pulmonary artery to measure various pressures inside the right atrium, right ventricle, and pulmonary artery.
Left atrial appendage occlusion: A minimally invasive procedure to seal off the left atrial appendage on the top left chamber of your heart in order to reduce the risk of stroke from an arrhythmia known as atrial fibrillation (aFib).
Pacemaker/defibrillator implant: A pacemaker is a device that is typically placed near the collarbone and uses electricity to stimulate your heart to beat; a defibrillator detects life threatening arrhythmias and can use an electrical impulse to restore a regular heartbeat.
Transcatheter heart valve implant/replacement: When a valve inside the heart is no longer working properly, this minimally invasive procedure delivers a new valve to the affected area of the heart using a catheter. Valve replacement is done on the aortic and tricuspid valves, and a select few patients with mitral valve disease. Transcatheter valve repair can be performed on the mitral and tricuspid valves.
Coronary stent placement: Coronary stents are small metal or mesh tubes inserted into the arteries that supply blood to the heart. If a lesion or blockage is limiting flow to heart muscle, an interventional cardiologist can deploy a stent to this area using a catheter inserted through the radial or femoral arteries.
Patent foramen ovale (PFO) closure: After birth, this opening normally closes. While it usually doesn’t cause any problems, patients who do have issues from a PFO can close it.
This procedure uses a medical device to close an opening between the two upper chambers of the heart. It can be delivered through a catheter inserted into a vein in the leg.
Balloon pump: This may be placed if your heart is not pumping enough blood to the rest of your body. The balloon is attached to the tip of a catheter and inserted into the aorta. The other end of the catheter attaches to a computer that regulates the inflation and deflation of the balloon at the correct time of heart beats.
Impella device placement: An Impella device helps the heart pump blood more effectively, similar to a balloon pump. The Impella device is placed through a minimally invasive procedure traveling up an artery and into the left ventricle chamber of the heart, where it can help a weakened ventricle to pump blood into the aorta and the rest of your body.
Balloon valvuloplasty: This procedure helps to open a stenotic (narrowed) heart valve using a balloon to expand the valve and improve blood flow. Using a catheter with a balloon on the end, a provider will guide the balloon to your affected valve and inflate it.
Electrophysiology
Ablation: Using heat generated by radiofrequency or extreme cold, a provider will guide a tiny catheter through your vein up to your heart to get rid of small pathways of electrical tissue that may be causing arrhythmias or other issues.
Electrophysiology study: Heart providers will look at electrical activity in a patient’s heart to determine if they have an arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat.
Diagnostic imaging
Coronary angiogram: Using fluoroscopy, a doctor will feed a catheter through an artery up toward your heart, then inject contrast dye to see any potential narrowings or blockages of the heart arteries.
“Each patient should know they are in good hands because everyone working in the cath lab is a well-trained professional who routinely does all of these procedures and is there to be involved,” Macikowski said. “The team is performing them all day, every day. Each person will be well cared for by a team of experts.”